Historical artifacts, sculptures, and architectural elements are invaluable pieces of cultural heritage, but time, environmental factors, and handling can lead to deterioration. Traditional restoration and archiving methods require meticulous craftsmanship, yet they can be time-consuming and invasive. With advancements in 3D scanning technology, preservation efforts have become more efficient and accessible, allowing professionals and enthusiasts alike to document and restore historical objects with remarkable quality.

The Role of 3D Scanning in Restoration and Archiving
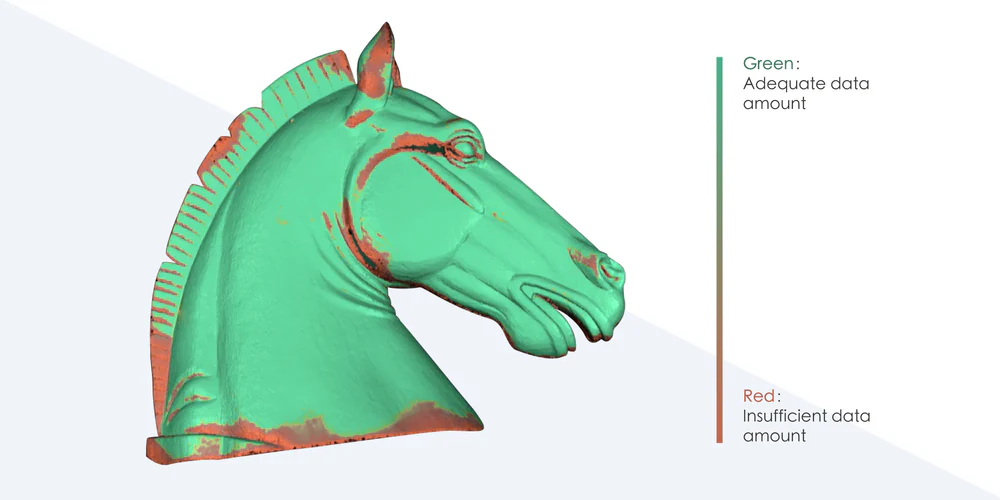
3D scanning captures the precise geometry and texture of historical artifacts, creating a digital model that can be analyzed, restored, or replicated. Unlike manual measurement techniques, which may introduce errors, 3D scanning provides a non-contact, high-resolution solution that minimizes the risk of further damage to fragile objects. This is particularly beneficial for conservators who need to assess wear and plan restoration work while maintaining the integrity of the original piece.
Digitally Restoring Damaged Artifacts
In cases where artifacts are incomplete or damaged, 3D scanning helps reconstruct missing elements by referencing similar structures or archived models. For example, a broken statue can be scanned, and the missing sections can be digitally recreated before being physically restored. This approach ensures a historically faithful restoration while allowing for virtual experiments before making irreversible modifications.
Archiving for Future Generations
Creating digital archives of cultural artifacts is a crucial aspect of preservation. Museums and researchers use 3D scanning to produce detailed records of sculptures, tools, and even architectural structures. These digital files can be stored indefinitely, shared globally, and even used for virtual museum exhibits, making historical artifacts more accessible to scholars and the public without exposing the originals to potential damage.
Making 3D Scanning Accessible
While industrial-grade 3D scanning equipment is often associated with large institutions, consumer-friendly options like EINSTAR's portable 3D scanners make this technology more accessible. Designed for small studios, researchers, and hobbyists, EINSTAR and EINSTAR VEGA provide great scanning capabilities without the complexity or cost of high-end industrial systems. These scanners allow users to create detailed digital models of historical items with ease, supporting personal and small-scale restoration projects.
Enhancing Public Engagement with History
Beyond professional restoration and archiving, 3D scanning fosters public interest in cultural heritage. Educational institutions and museums can create interactive experiences, such as 3D-printed replicas or virtual reality exhibits, giving audiences an immersive way to explore history. By digitizing historical artifacts, institutions can also facilitate research collaborations and offer more inclusive access to heritage materials.
Conclusion
3D scanning has transformed the way historical artifacts are preserved, restored, and shared. By capturing precise digital models, professionals and hobbyists alike can contribute to the safeguarding of cultural heritage. With accessible scanning solutions like EINSTAR, small studios and individuals can participate in preservation efforts, ensuring that the past remains tangible for future generations.






Share:
How 3D Scanning Supports Personalization in Product Design
Optimizing DIY and Home Repair Projects with 3D Scanning