EINSTAR Academy: Ihr Leitfaden zum 3D-Scannen
3D-Scanning entwickelt sich branchenübergreifend zu einer beliebten Lösung – von der Fertigung und dem Gesundheitswesen bis hin zu Kunst, Bildung und Forschung. Dank des berührungslosen Workflows, der hohen Präzision und des breiten Anwendungsspektrums ist es zugänglicher denn je.
Bei so vielen verfügbaren Scannertypen und Spezifikationen kann die Auswahl des richtigen Scanners jedoch überwältigend sein. Hier kommt die EINSTAR Academy ins Spiel. Diese technische Kolumne im EINSTAR-Forum liefert nicht nur Tipps zum Scannen und zur Produktauswahl, sondern bietet auch Expertenwissen, das Ihnen hilft, die Komplexität der 3D-Scantechnologie zu meistern – damit Sie intelligenter, schneller und sicherer scannen können.
01. Was ist 3D-Messung?
Beim 3D-Scannen werden Licht und Sensoren verwendet, um die Form, Größe und Textur eines Objekts zu erfassen und reale Objekte in digitale 3D-Modelle umzuwandeln.
Es gibt zwei Hauptarten der 3D-Messung:
- Kontaktmessung: Erfordert das Berühren des Objekts. Sie ist sehr genau, aber langsam und nicht ideal für weiche oder große Gegenstände. Beispiel: Koordinatenmessgeräte (KMG).
- Berührungslose Messung: Verwendet Licht zum berührungslosen Scannen. Strukturiertes Lichtscannen ist schnell, präzise und eignet sich hervorragend zum Scannen komplexer Objekte aller Größen.

02. Strukturlicht-3D-Scanning
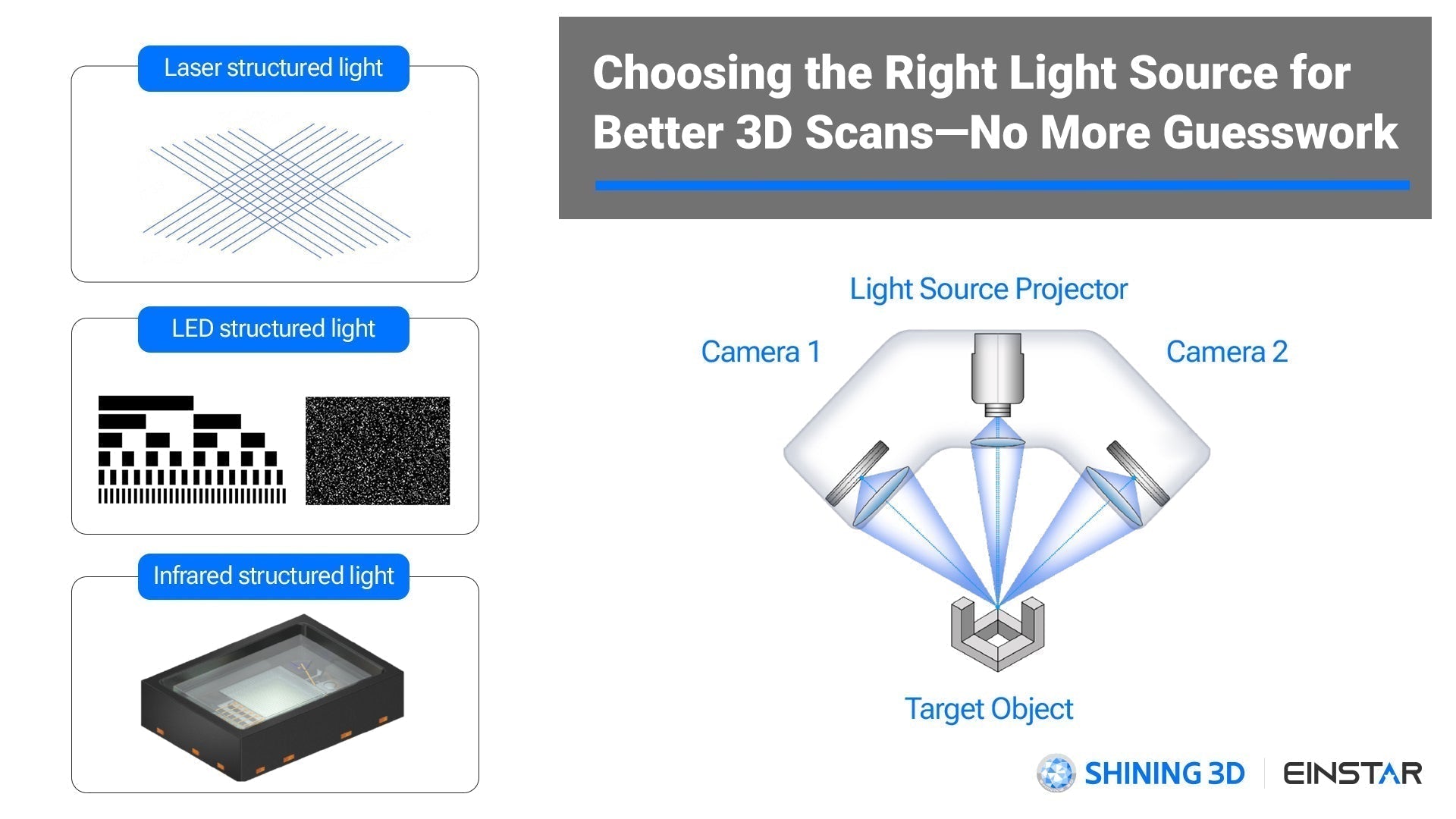
Funktionsweise und Lichtquellentypen
Strukturiertes Licht-3D-Scannen basiert auf optischer Triangulation. Ein Projektor wirft ein gemustertes Licht auf die Oberfläche des Objekts, während Kameras erfassen, wie sich das Muster über die Form verformt.
Durch die Analyse dieser Verformungen berechnet das System die 3D-Geometrie des Objekts und generiert eine Punktwolke – eine digitale Karte der Oberfläche.
Bei dieser Methode werden unterschiedliche Lichtquellen (z. B. Laser, LED, Infrarot) verwendet, die jeweils für bestimmte Scananforderungen wie Präzision, Texturerfassung oder Materialanpassung geeignet sind.

🔦 So wählen Sie die richtige Lichtquelle für 3D-Scanner mit strukturiertem Licht
Nicht alle 3D-Scanner verwenden die gleiche Lichtquelle – und die Wahl der richtigen Lichtquelle kann Ihre Scanergebnisse erheblich beeinflussen. Hier finden Sie eine Kurzanleitung zu den drei gängigsten Lichtquellentechnologien und ihren idealen Anwendungsfällen:
1. Laserlinienscanning

- Messtechnische Genauigkeit für anspruchsvolle industrielle Inspektionen
- Starke Entstörungsleistung; funktioniert gut auf schwarzen oder reflektierenden Oberflächen
- Hohe Scan-Effizienz mit großem Scan-Bereich und fortschrittlichen Algorithmen (z. B. erreicht EinScan RIGIL bis zu 70 fps)
- Geeignet für den Außenbereich
- Erfordert normalerweise Markierungen, obwohl einige Modelle das markierungsfreie Scannen unterstützen
Geeignet für:
Große Industrieteile, Automobilrohre, Formen, kulturelle Artefakte und Objekte, die komplex oder schwer zu berühren sind
Vertreter: EinScan Rigil
2. Weißes LED-Strukturlicht (Streifen- oder Speckle-Projektion)
① Streifenbasiertes 3D-Scanning mit strukturiertem Licht
Hauptmerkmale:
- Hohe Genauigkeit und Auflösung für kleine bis mittelgroße Präzisionsteile
- Kompatibel mit automatisierten Drehtischen für effizientes Scannen
- Farbkameras unterstützen die Texturerfassung mit hervorragender Farbtreue (Beispiel: Transcan C verfügt über zwei professionelle Farbkameras, die Texturkarten mit bis zu 12 MP für eine äußerst realistische Farbwiedergabe liefern).
- Ausgestattet mit hochauflösenden Industrieobjektiven für detailreiche Oberflächen und präzise 3D-Rekonstruktion
Geeignet für:
Präzisionsteileprüfung, Produktdesign, digitale Archivierung und Anzeige
Vertreter: Transcan C, EinScan SE2, EinSan SP2

② Speckle-basiertes 3D-Handscannen
Hauptmerkmale:
- Reibungslose Datenerfassung durch fortschrittliche Algorithmen und stabile visuelle Sensoren – tragbar, effizient und verzögerungsfrei
- Hervorragende Farbwiedergabe mit professionellen RGB-Kameras, die Oberflächenstruktur und Farbe in Echtzeit erfassen
- Unterstützt mehrere Ausrichtungsmodi; Oberflächen mit vielen Details oder Strukturen können ohne Markierungen gescannt werden
Geeignet für:
Kunst und Kultur, Medizin, Orthetik und Prothetik, Bildung und Forschung und anderes 3D-Design.
Vertreter: EinScan Medixa
 3. Infrarot-VCSEL
3. Infrarot-VCSEL

Infrarot-VCSEL-Laser sind unsichtbare Lichtquellen. Hochwertige VCSEL-Infrarot-Laserprojektoren projizieren strukturiertes Licht mit spezifischen Merkmalen auf das zu scannende Objekt (das Licht ist für das menschliche Auge unsichtbar). Spezielle Infrarotkameras erfassen das reflektierte Licht und erfassen dreidimensionale Rauminformationen des Objekts. Anschließend verarbeitet Software diese Informationen, um Bilder zu erzeugen und ein 3D-Punktwolkenmodell zu rekonstruieren.
Hauptmerkmale:
- Ideal zum Scannen des menschlichen Körpers und für den Einsatz in der Bildung
- Augenschonende, weiche Beleuchtung, die für die Motive angenehm ist
- Unterstützt Handheld-Scannen; leicht und einfach zu bedienen
- Gute Leistung auf schwarzen oder glänzenden Oberflächen
Geeignet für:
Humanmodellierung, Lehre und Forschung, Rapid Prototyping
Vertreter: EINSTAR, EINSTAR VEGA


Diese Lichtquellenmodi stellen den Großteil der derzeit auf dem Markt erhältlichen 3D-Scanner dar. Jeder Ansatz – ob Streifen-, Speckle- oder Laserlinienscanning – bietet je nach Anwendung unterschiedliche Vorteile und Einschränkungen. Von der hochpräzisen industriellen Inspektion bis zur vollfarbigen Digitalisierung des menschlichen Körpers können Anwender die passende Lösung basierend auf ihren spezifischen Scananforderungen, Objekteigenschaften und Arbeitsumgebung auswählen.
Wenn Sie Hilfe bei der Scannerauswahl benötigen, besuchen Sie www.einstar.com für eine kostenlose Beratung! Dort stehen Ihnen viele Experten zur Verfügung, die Ihre Fragen zur Modellauswahl beantworten!






Share:
Schnelleres 3D-Scannen gewünscht? Diese 4 Faktoren könnten Ihnen Stunden sparen.
So scannen Sie ein Auto mit EinScan Rigil in 3D (auch Autoteile)